
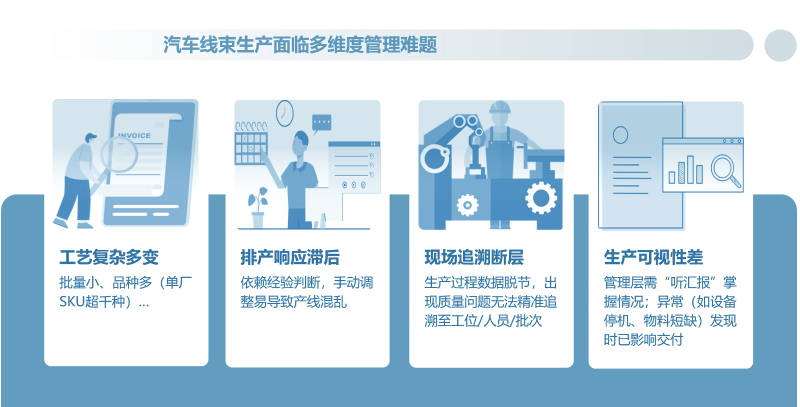
Complex and variable processes lead to low analysis efficiency: The process parameters (wire diameter, terminal type, waterproof requirements, etc.) are numerous and complex. Paper-based management is prone to loss and difficult to trace.
Low production scheduling efficiency and delayed response: Manual production scheduling takes more than 1 hour and relies on experience-based judgment; in the face of demands such as order insertion and combined production, it is unable to quickly match equipment and process requirements.
Barcode management is chaotic, with a lack of traceability: The barcode rules across different workshops are not unified (engraving/paper/batch), and there is a disconnect between production process data and barcode binding. This results in a lack of precise traceability to workstations, personnel, and batches in case of quality issues.
Lagging quality control and high compliance risks: Data such as crimping tension and conductivity testing rely on manual recording, which is prone to errors and difficult to verify in real time, often resulting in near-term/non-conforming products flowing into the downstream.
Poor production visibility and slow response to anomalies: Data such as production progress, equipment status, and WIP (Work-in-Process) flow are scattered, requiring management to rely on "reporting" to grasp the situation; by the time anomalies are discovered, they have already affected delivery.
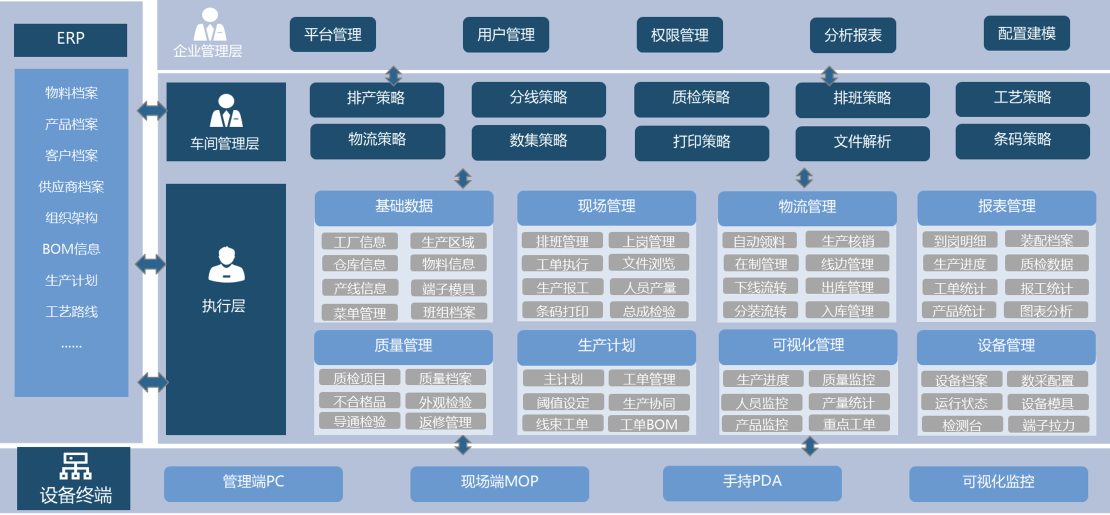
Integrating digital process analysis, intelligent production scheduling, full traceability through barcodes, equipment interconnection, and closed-loop quality control;
Build an integrated management platform for "planning-execution-monitoring-analysis";
Solve the problems of "disorder, slowness, poor quality, and discontinuity" in wire harness production;
Achieve full-process transparency and intelligent operation.
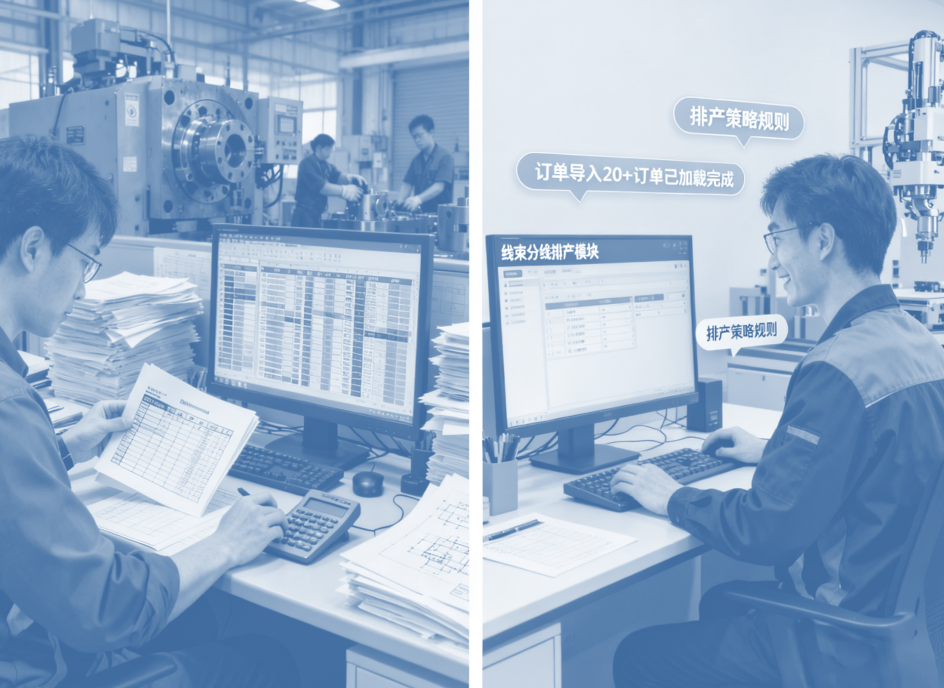

Daily production scheduling has evolved from "manual calculation in 1 hour" to "automatically generating plans in 15 minutes"
In the past: Faced with dozens of sales orders, it was necessary to manually verify process documents (wire diameter, terminal model), equipment capacity, and inventory. The production scheduling plan took 1.5 hours to determine, and frequent equipment mold changes often occurred due to the omission of calculating the "combined production threshold".
Now: Open the system's "Wire Harness Sorting and Production Scheduling Module". After importing the order, the system automatically analyzes it and combines with preset production scheduling strategies (such as "combined production for wire diameters ≥ 0.75mm" and "dedicated equipment for waterproof terminals"). An optimized production scheduling plan is generated within 15 minutes and simultaneously pushed to each production line terminal.
Emergency order insertion: from "frantically adjusting plans" to "one-click rearrangement without chaos"
In the past: When a temporary order was inserted, it required manual adjustment of the already scheduled 10+ work orders, which could easily lead to disconnection between the front and back processes, resulting in production line downtime of over 1 hour.
Now: Mark "Emergency Order" in the system, click "Quick Re-scheduling", and the system will automatically prioritize the allocation of idle equipment. Simultaneously, it will update the material requirements (such as terminals and sheaths) and push them to the warehouse. The adjustment can be completed in 3 minutes, ensuring seamless connection of the production line.

Production monitoring transforms from an "information black hole" to a "transparent display screen"
In the past: To inquire about the progress of each production line, one had to separately consult the team leader, only to receive vague responses like "Almost done" or "Still waiting for materials", making it impossible for overall coordination.
Now: Open the "Workshop Visualization Screen", and the real-time progress of each production line (such as "85% completion of the assembly line in Harness Workshop 1"), the quantity of work in progress (such as "300 units in inventory after crimping"), and abnormal items (such as "1 material shortage") are all clearly visible. Clicking on an abnormal item allows you to view the details and dispatch a task for handling.
Exception handling has evolved from "delayed firefighting" to "real-time intervention"
In the past: When there was a "terminal shortage" on the production line, the team leader reported it only after 1 hour, resulting in a 2-hour production line shutdown and affecting the daily delivery.
Now: The system monitors the inventory in the line-side warehouse in real-time. When the number of terminals falls below a safety threshold (such as 50), an automatic pop-up alert is triggered. Director Liu immediately coordinates with the warehouse for replenishment, which is delivered within 15 minutes, with no downtime losses.

Automatic decomposition of the master production schedule (docking with SAP orders).
Configuration of wire harness branching and production scheduling strategy (based on wire diameter, terminal, and batch threshold).
Emergency order insertion, rapid rearrangement, and conflict warning.
Visual preview and one-click issuance of production scheduling plans.
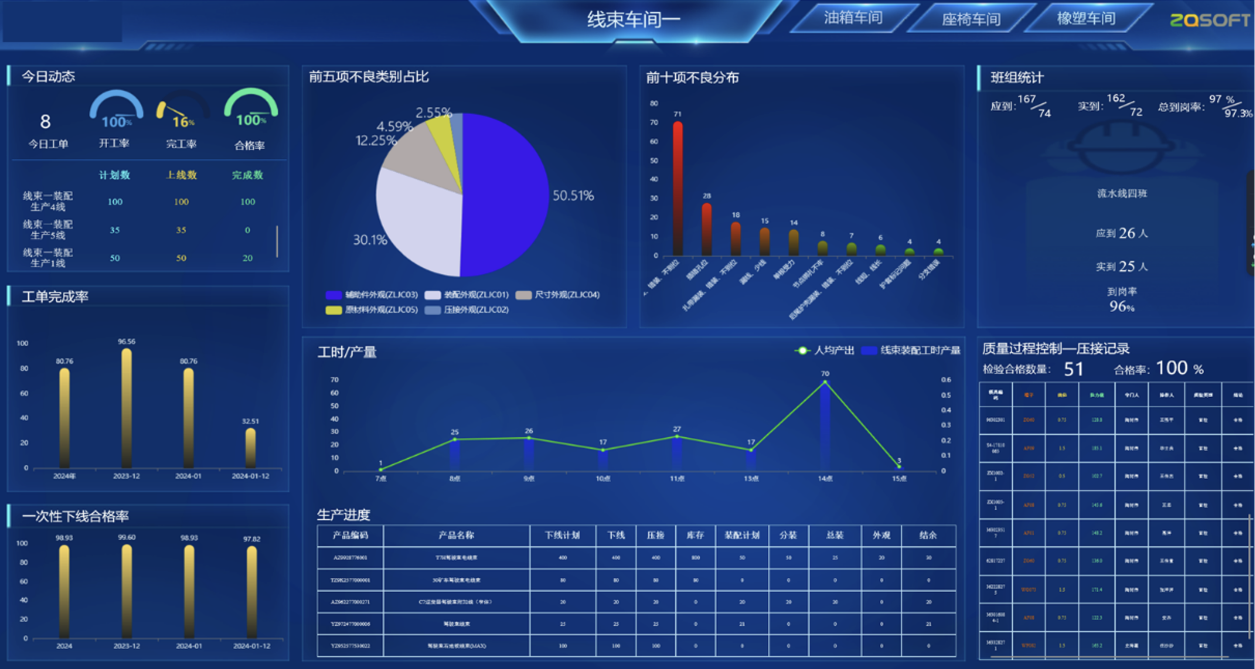
Three-level large screens at workshop level/production line level/workstation level.
Real-time display of production progress, quality, and equipment status.
Pop-up alerts for abnormal items (material shortages, equipment failures).
Production: Order delivery rate, production line efficiency, and work-in-process turnover rate.
Quality indicators: pass rate, defect analysis, quality inspection coverage.
Equipment: OEE, MTBF, maintenance cost.
Personnel category: workstation utilization rate, performance achievement rate.

1883D6D19D79454E9B3FA44C8F7F50F7.png)